Abstract
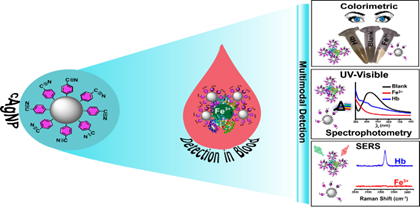
Iron detection is one of the critical markers to diagnose multiple blood-related disorders that correspond to various biological dysfunctions. The currently available anemia detection approach can be used only for pre-treated blood samples that interfere with the actual iron level in blood. Real-time detection approaches with higher sensitivity and specificity are certainly needed to cope with the commercial level clinical analyses. Herein, we presented a novel strategy to determine the blood iron that can be easily practiced at commercial levels. The blend of well-known iron-cyanide chemistry with nanotechnology is advantageous with ultrahigh sensitivity in whole blood analysis without any pre-treatments. This approach is a combined detection system of the conventional assay (UV-visible spectroscopy) with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Organic cyanide modified silver nanoparticles (cAgNPs) can selectively respond to Fe3+ ions and Hb protein with a detection limit of 10 fM and 0.46 µg/mL, respectively, without being affected by matrix interfering species in the complex biological fluid. We confirmed the clinical potential of our new cAgNPs by assessing iron-status in multiple anemia patients and normal controls. Our SERS-based iron quantitation approach is highly affordable for bulk-samples, cheap, quick, flexible, and useful for real-time clinical assays. Such a method for metal-chelation has extendable features of therapeutics molecular tracking within more complex living systems at cellular levels.
DOI: 10.1039/x0xx00000x
